Understanding Ebola Virus Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention
BlogTable of Contents
- ASLM Ebola Outbreak: Laboratory Workers as Key Partners
- Ebola DNA sequenced to track outbreak | WIRED UK
- Ebolavirus - Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre
- Ebola treatment studies to begin by December
- Ebola | Johns Hopkins Medicine
- U.Va. Team Identifies, Maps Unique Structure Within Deadly Ebola Virus ...
- What is Ebola?
- A Photographer Documents Ebola’s Deadly Spread - The New York Times
- What Happens After Surviving Ebola? | SiOWfa14 Science in Our World ...
- American ERs prepare as Ebola and Ebola fear spreads - CNN
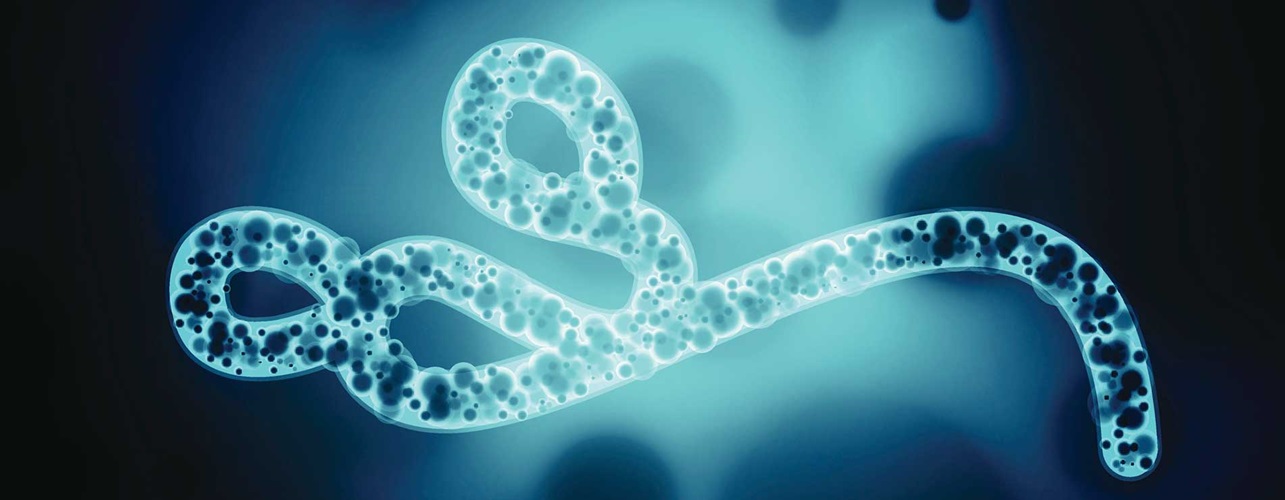
The Ebola virus disease, also known as Ebola hemorrhagic fever, is a severe and often deadly illness caused by the Ebola virus. According to WebMD, Ebola is a rare but highly infectious disease that can spread quickly through human-to-human contact. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of Ebola virus disease, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this deadly illness.
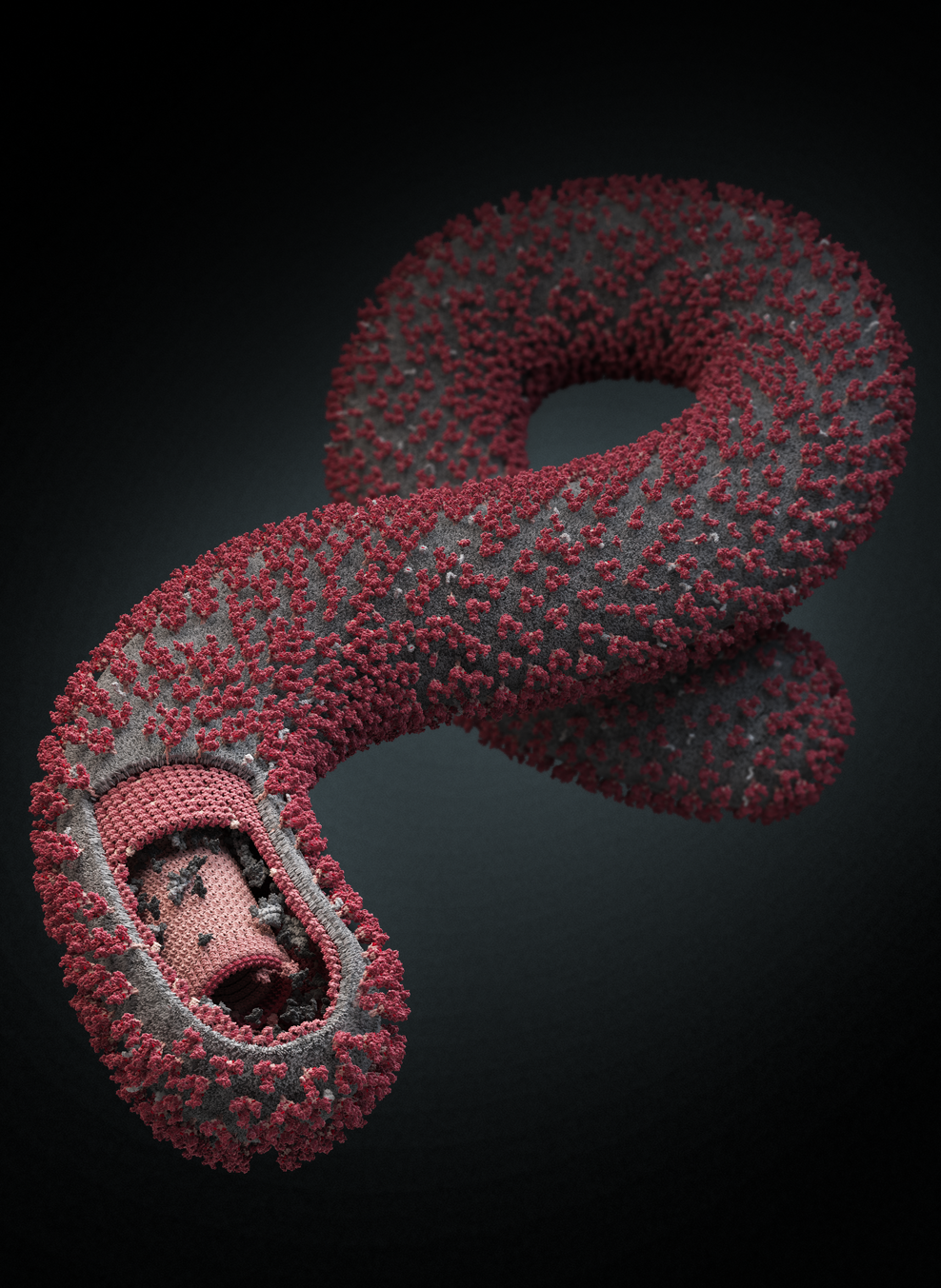
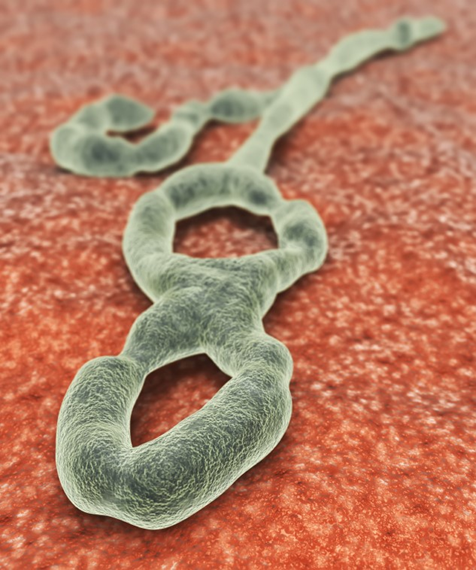
What is Ebola Virus Disease?
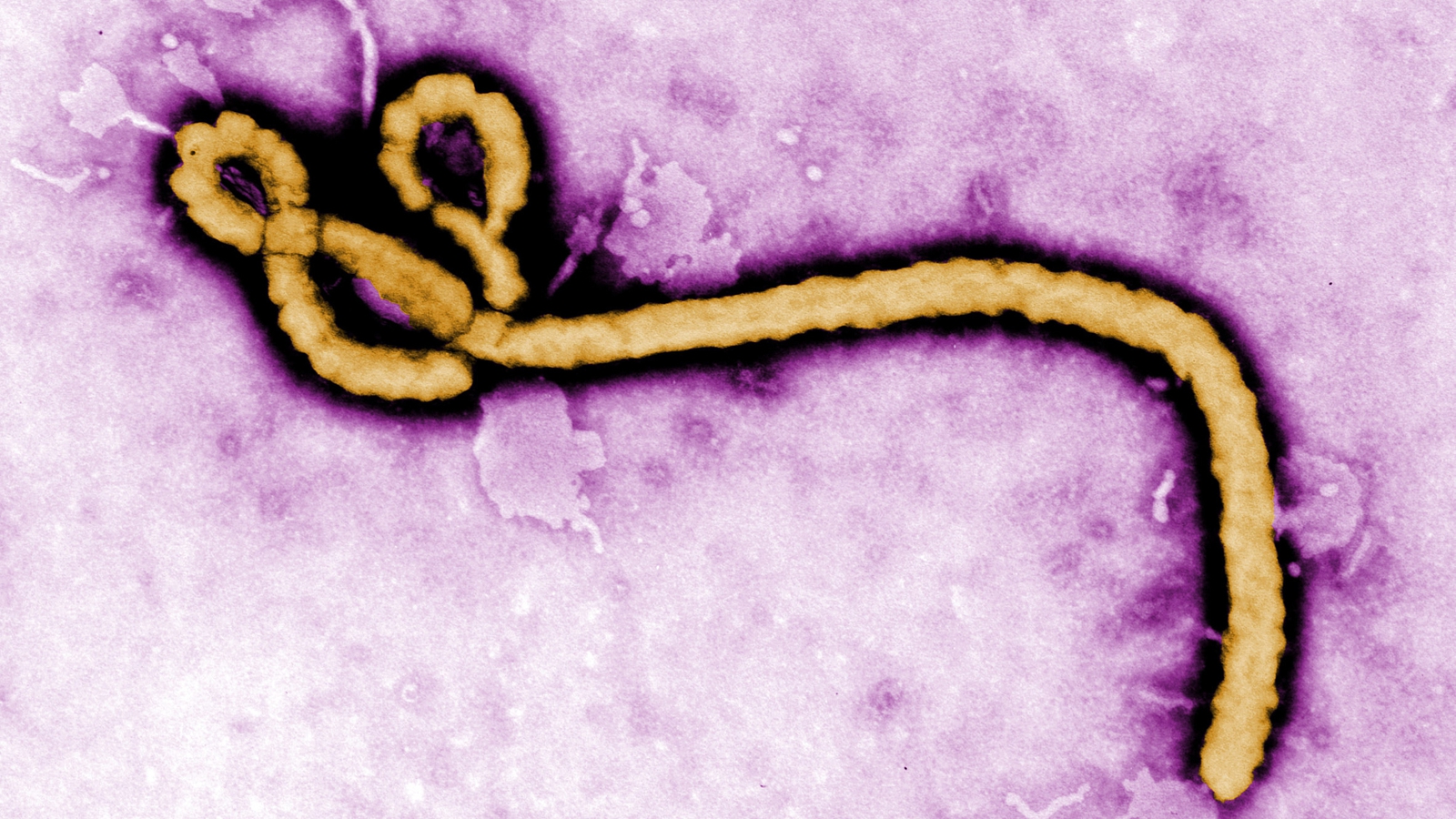
Ebola virus disease is a viral illness that affects humans and non-human primates, such as monkeys and gorillas. The virus is named after the Ebola River in the Democratic Republic of Congo, where it was first identified in 1976. Ebola is a member of the Filoviridae family of viruses, which also includes the Marburg virus. The virus is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood, sweat, and saliva.

Causes of Ebola Virus Disease

According to WebMD, the exact cause of Ebola virus disease is still unknown, but it is believed to be linked to the handling and consumption of infected animals, such as fruit bats and non-human primates. The virus can also spread through human-to-human contact, including:

- Direct contact with infected bodily fluids, such as blood and sweat
- Touching contaminated surfaces and objects
- Close contact with an infected person, such as hugging or shaking hands
Symptoms of Ebola Virus Disease
The symptoms of Ebola virus disease can vary, but they typically include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Weakness
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Bleeding or bruising
According to WebMD, the symptoms of Ebola can appear anywhere from 2 to 21 days after exposure to the virus. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Prevention and Treatment of Ebola Virus Disease
Preventing the spread of Ebola virus disease is crucial to controlling outbreaks. Some effective prevention methods include:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing your hands frequently with soap and water
- Wearing protective clothing, such as gloves and masks, when caring for an infected person
- Avoiding close contact with infected people and animals
- Getting vaccinated against Ebola, if available
Treatment for Ebola virus disease typically involves supportive care, such as providing fluids and electrolytes, and managing symptoms. According to WebMD, there is no specific cure for Ebola, but early treatment can improve survival rates.
In conclusion, Ebola virus disease is a severe and often deadly illness that can spread quickly through human-to-human contact. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and prevention methods of Ebola is essential to controlling outbreaks and saving lives. By practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected people and animals, and getting vaccinated, if available, we can reduce the risk of contracting Ebola virus disease. If you suspect you have been exposed to Ebola or are experiencing symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
For more information on Ebola virus disease, visit WebMD or consult with a healthcare professional.